Vitamin D also known as calciferol, is a fat-soluble vitamin found in foods, supplements, and produced within the body from UV rays.1 The body must activate it from those sources, first in the liver, then kidneys to the form known as calcitriol.
Vitamin D promotes bone growth, calcium absorption in the gut and maintains sufficient levels of serum calcium and phosphate. This helps to allow normal bone mineralization and prevent cramps and spasms due to low calcium levels.1 Vitamin D can prevent our bones from becoming brittle and thin which prevents osteoporosis in adults (with calcium).
Vitamin D is also involved in reducing inflammation, processes of cell growth, immunity, glucose metabolism. This could be due to the fact that many tissues have Vitamin D receptors. Regarding immunity, Vitamin D receptors are “expressed on the immune cells such as B cells, T cell, and antigen-presenting cells.”2 Further, Vitamin D may “increase the levels of T regulatory cells” as these cells suppress the immune response leading to a stable state in the body.2
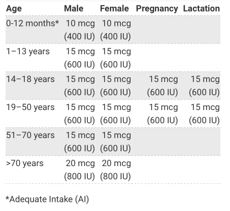
There are two main forms of Vitamin D, D2 ergocalciferol and D3 cholecalciferol. Both forms are well absorbed in small intestines and this is not affected by age or obesity. When looking at Vitamin D strengths, an important conversation to remember is 1mcg = 40 IU (International Units). Below is the recommendation for Vitamin D daily intake, categorized by age group and sub-populations.
Table 1. Recommended Dietary Allowance for Vitamin D.1
“Few foods naturally contain vitamin D. The flesh of fatty fish such as trout, salmon, tuna, and mackerel and fish liver oils are among the best sources.”1 Another source of Vitamin D is through direct exposure to sunlight. Most experts recommend about 5-30 minutes of sun exposure especially between 10 a.m. – 4 p.m. twice a week without out the use of sunscreen.1 The final source is found in supplements, either as Vitamin D2 or D3. “However, most evidence indicates that Vitamin D3 increases serum Vitamin D levels to a greater extent and maintains these higher levels longer than Vitamin D2.”1 Further, Vitamin D2 is derived from plants and Vitamin D3 comes from animals.
Some groups at risk include breastfed infants and this is because human milk does not meed the Vitamin D requirements. Older adults are at risk because the skin’s ability to synthesize vitamin D decrease with age. People with limited sun exposure (homebound, long robes, dresses) also puts them at risk. People with dark skin are at risk because there is a greater amount of the pigment melanin in the out-layer of the skin which reduces the ability to produce as much Vitamin D.1 Vitamin D deficiency can cause rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, both conditions result in softening of the bones.3 Excessive Vitamin D can be harmful as well due to vitamin D increasing Ca absorption in the gastrointestinal tract causing hypercalcemia leading to “nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, excessive thirst…in extreme cases, renal failure.”1
Here at Prescott Compounding Pharmacy we offer of Pure Encapsulations Vitamin D capsule and liquid dropper forms, additionally they are gluten and GMO free.
By Jimmy Stevens, Pharm. D.
References
- Vitamin D. https://ods.od.nih.gov. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/. Last Reviewed August 17th, 2021. Accessed March 9th, 2022.
- Vitamin D. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/supplements/vitamin-d/. Last reviewed April 21th, 2021. Accessed March 9th, 2022.
- Print Book. 2022. Chapter 49.
